
In the rapidly evolving landscape of energy technology and sustainable innovation, Pisphere stands out as a beacon of promise and ingenuity. Founded by a visionary team from Seoul National University, Pisphere has pioneered a remarkable breakthrough with its Plant-Microbial Fuel Cell (Plant-MFC) technology. This unique advancement not only taps into natural processes to generate clean, renewable energy but also opens new avenues for sustainable development across Asia, particularly targeting the burgeoning markets in Southeast Asia.
The Genesis of Pisphere: Innovation Rooted in Academia
The journey of Pisphere began in the laboratories of Seoul National University, where a group of dedicated researchers sought to harness the untapped potential of microbial fuel cells integrated with plant systems. This fusion of biology and technology resulted in Plant-MFCs capable of producing continuous, 24/7 power by leveraging the natural microbial activity around plant roots. This innovation transcends traditional energy barriers by providing a low-cost, eco-friendly power source ideal for use in off-grid and resource-limited environments.
Unlike conventional solar or wind energy systems that are intermittent by nature, Pisphere’s Plant-MFC technology produces a steady stream of electricity regardless of weather conditions or time of day. This is a game-changer for regions in Southeast Asia where energy reliability and affordability remain major challenges.
The Core Technology: Plant-Microbial Fuel Cells
At the heart of Pisphere’s offerings lies the Plant-MFC system. This technology works by converting the organic compounds exuded by plant roots into electrical energy through the metabolic activity of microbes in the soil. The system is ingeniously simple yet incredibly effective, enabling continuous power generation without requiring any complex external inputs.
The process involves planting specific species known for robust root exudate production into specially designed units that capture the microbial electron transfer. The harvested energy is then harnessed to power small devices, sensors, or lighting solutions, creating a sustainable energy ecosystem.
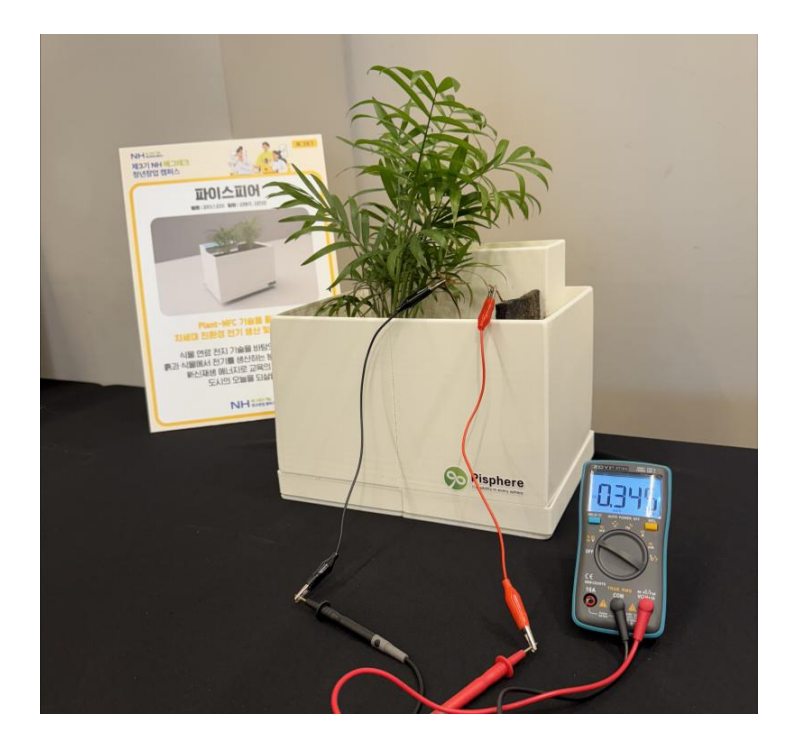

This synergy between plants and microbes makes the technology inherently sustainable and scalable. It also offers a low environmental footprint compared to fossil fuels or even some renewable options that require expensive infrastructure.
Affordability and Accessibility: The $10-15 Annual Cost Advantage
One of the most compelling aspects of Pisphere’s Plant-MFC technology is its affordability. The annual cost of maintaining a system ranges from just $10 to $15, positioning it as an accessible solution for communities that have long struggled with energy poverty.
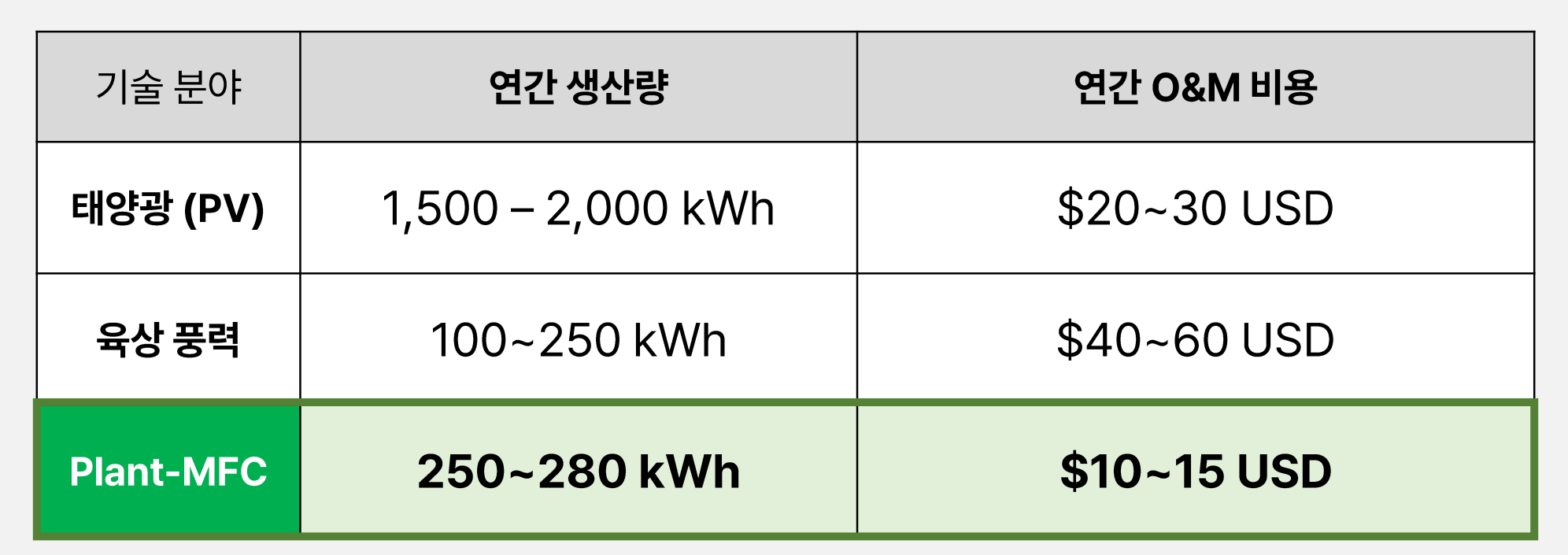
This cost efficiency stems from the minimal maintenance requirements and the self-sustaining nature of the system. Unlike traditional power sources that demand costly fuel or parts replacement, Pisphere’s technology thrives on natural biological processes, making it ideal for rural or remote regions where managing complex systems is impractical.
Targeting Asia: From Korea to Southeast Asia’s Energy Landscape
Pisphere’s vision extends well beyond its Korean origins. Recognizing the diverse energy needs across Asia, the company is focusing its expansion on Southeast Asia, a region witnessing rapid urbanization alongside persistent energy access challenges.
Countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, the Philippines, and Thailand present fertile ground for Pisphere’s technology. Here, vast rural populations still lack reliable electricity, and conventional grid expansion is often slow and costly. Pisphere’s Plant-MFC systems offer a decentralized, sustainable alternative that empowers communities by providing continuous power for lighting, communication, and essential devices.
Moreover, Southeast Asia’s tropical climate and abundant vegetation create ideal conditions for Plant-MFCs to flourish. The synergy between the local environment and the technology amplifies its effectiveness and adoption potential.
Applications Beyond Energy: Smart Cities and Urban Farming
Pisphere’s impact is not limited to rural electrification. The company envisions its technology as a cornerstone of next-generation smart city infrastructure and sustainable urban agriculture.
Smart City Integration
In urban centers, Pisphere’s Plant-MFCs can be integrated into green spaces, parks, and roadside landscaping to power IoT sensors, environmental monitoring devices, and street lighting. This not only reduces the city’s carbon footprint but also enhances the resilience of urban infrastructure.

By decentralizing power production and embedding it into living systems, Pisphere supports the development of smart cities that are eco-conscious and energy-efficient.
Urban Farming and Sustainability
The company also champions the use of Plant-MFC technology in urban farming initiatives. As cities seek to increase their food security and reduce supply chain emissions, urban farms have become critical.
Pisphere’s systems can power sensors that monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and climate conditions in urban farms, enabling precision agriculture without adding to the energy grid’s burden.

This integration fosters a circular ecosystem where energy and food production coexist harmoniously.
Environmental and Social Impact
Pisphere’s technology offers tangible benefits that go beyond economics and engineering. It aligns with global sustainability goals by promoting renewable energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Environmental Benefits
- Carbon Neutrality: Using living plants and microbes means the system’s carbon footprint is minimal.
- Soil Health: The Plant-MFC systems encourage the maintenance of healthy microbial populations in the soil.
- Biodiversity: These systems promote biodiversity by integrating living components into energy infrastructure, unlike conventional systems that can disrupt ecosystems.
Social Benefits
- Energy Access: By lowering costs and increasing reliability, Pisphere addresses energy poverty.
- Community Empowerment: Local communities can manage and maintain these systems, fostering a sense of ownership and technical skill development.
- Health Improvements: Reliable lighting and power reduce reliance on hazardous fuels like kerosene and candles, improving indoor air quality and safety.

Challenges and Future Outlook
While Pisphere’s Plant-MFC technology is groundbreaking, scaling it across diverse Asian markets involves challenges:
- Market Education: Convincing communities and governments to adopt a relatively novel technology requires extensive outreach and demonstration projects.
- Infrastructure Synergy: Integrating Plant-MFCs with existing grid and off-grid solutions necessitates smart design and regulatory support.
- R&D for Optimization: Continuous improvement in energy output and system durability will be critical for long-term success.
Despite these hurdles, Pisphere is well-positioned to lead a green energy revolution. Partnerships with local governments, NGOs, and private sectors are already in progress, propelling the technology from controlled environments to real-world applications.
Conclusion
Pisphere epitomizes the spirit of innovation harnessed by academic excellence and entrepreneurial vision. From its roots in Korea, the company is poised to transform Southeast Asia’s energy paradigm with its Plant-MFC technology—delivering affordable, reliable, and sustainable power.
The convergence of biology and technology embodied by Pisphere offers a hopeful blueprint for the future, where clean energy is accessible to all, and nature itself becomes an ally in powering human progress.
As Pisphere continues to expand, its global vision serves as a reminder that solving pressing energy challenges requires not only advanced technology but also thoughtful integration with natural ecosystems and communities.
This journey from the heart of Seoul National University to the fields and cities of Southeast Asia marks the beginning of a new chapter in sustainable development—one powered by plants, microbes, and the pioneering spirit of innovation.